Low-Code Guide 2025: Efficient Development without programming knowledge

How can companies develop innovative applications in 2025 without writing a single line of code? The pressure to digitize is growing, while the shortage of skilled workers slows implementation. This is exactly where low-code comes in: With visual platforms, custom solutions are created even without programming knowledge—quickly, efficiently, and flexibly. In this guide, you’ll learn step by step how low-code becomes a game changer. From definition and benefits to practical tips—discover how to automate processes and secure real competitive advantages for your company.
What is Low-Code? Definition, distinction, and fundamentals
Low-code is more than a buzzword—it describes a revolution in software development. But what really lies behind the term, and how does low-code differ from other approaches?
Definition and history
Low-code platforms are visual development environments that let you build applications using graphical elements instead of traditional programming. The concept clearly differs from no-code (completely without code) and traditional software development. Its origins can be traced back to the 1980s with 4GL and Rapid Application Development tools.
In 2014, Forrester Research coined the term low-code, which has since become synonymous with citizen development and visual modeling. In recent years, the technology has evolved rapidly: from early platforms like OutSystems or Mendix to modern solutions with AI integration. If you want a deeper dive, you’ll find a solid overview at Low-Code-Entwicklung: Definition und Vorteile.
How does low-code work?
At the heart of low-code is the visual user interface. Instead of writing code line by line, you use drag-and-drop to assemble components and modules. Development is model-based: data structure, business logic, and user interface are defined graphically.
Reusable templates and widgets save time. You connect external data sources via REST APIs. This allows business processes to be automated. Modern low-code platforms support you throughout the entire app lifecycle—from idea to rollout.
Low-code vs. no-code vs. traditional development
Low-code is aimed at IT professionals, power users, and business departments. No-code is primarily intended for non-technical users, while traditional development requires deep programming expertise. Differences become apparent in customization and project complexity.
| Approach | Target group | Customizability | Complexity | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-code | IT, business units | High | Medium | Process automation |
| No-code | Business users | Low | Low | Form-based apps |
| Traditional | Developers | Very high | High | Custom solutions |
Low-code can be combined with traditional methods—especially when complex requirements arise. Gartner estimates that by 2024 around 65% of all software projects will rely on low-code.
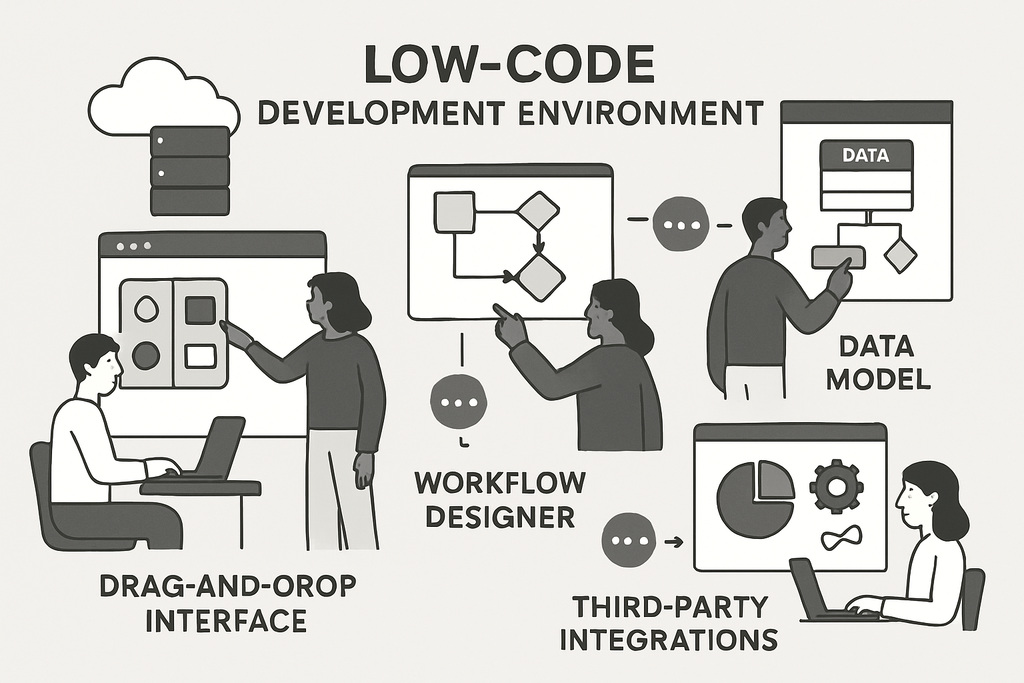
Typical components of a low-code platform
A powerful low-code platform offers you:
- A visual development environment (IDE) with drag-and-drop functionality
- Database and data modeling tools
- Workflow and process designers for automation
- Graphical user interface editor (GUI builder)
- Integration options for third-party applications (e.g., ERP, CRM)
- Templates, widgets, plug-ins, and an app marketplace
- Flexible deployment in the cloud or on-premises
These components enable rapid development, easy integration, and seamless extensibility for a wide variety of enterprise requirements with low-code.
Advantages of low-code: Efficiency, speed, and innovation
Low-code is revolutionizing how companies develop software. You benefit from significantly greater efficiency, speed, and innovation. Instead of months-long development phases, tailored solutions are created in record time—and without traditional programming skills.
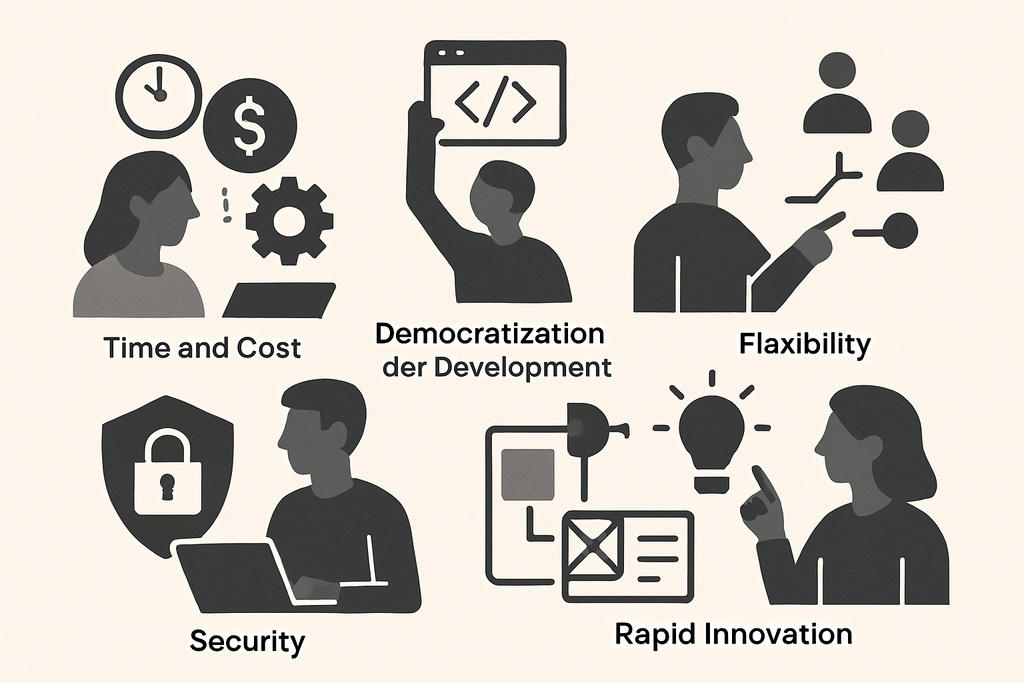
Time and cost savings
With low-code, the development cycle is drastically shortened. Applications that once took weeks or months can now be ready in days. Visual modeling replaces error-prone manual code. Reusable components and templates save additional resources.
Companies need fewer specialized developers. This reduces costs for development, maintenance, and enhancements. Automated processes ensure that routine tasks run almost by themselves. Prototyping becomes child’s play—and sources of error are minimized.
According to Forrester, the market volume for low-code already exceeded USD 21 billion in 2022. You can find a detailed overview of the benefits in Die 5 wichtigsten Vorteile von Low-Code.
Democratizing software development
Low-code turns software development into a team effort. Citizen developers from business departments can create and adapt their own applications. This overcomes bottlenecks caused by the shortage of IT specialists—and fuels innovation.
Departments like HR or Finance can independently develop workflows without relying on external service providers. Collaboration between IT and the business is strengthened. In this way, low-code accelerates digitization across all areas of the company.
You benefit from greater initiative and an enhanced culture of innovation within the company. Barriers to entry are low, and the impact is huge.
Flexibility and scalability
Low-code platforms are flexible and grow with your needs. Changes to workflows or forms are implemented in minutes rather than days. Scalable cloud or on-premises solutions adapt dynamically to business growth.
Existing systems like SaaS or legacy applications can be integrated without difficulty. Reusable modules save time on new projects. Whether web, mobile, or desktop—low-code enables cross-platform development without duplicate effort.
Examples show that adapting business processes is easier than ever before. And with every additional project, efficiency increases.
Quality, security, and governance
Quality is a focus of low-code. Integrated testing tools and automated rollbacks ensure reliable applications. Compliance requirements such as GDPR are met through centralized management and audit trails.
Governance features control permissions and access across the enterprise. Standardized components reduce security risks. Changes are logged, ensuring transparency and control at all times.
This results in robust solutions that meet the highest standards of security and quality. Companies can rely on smooth operations.
Innovation through faster prototypes and MVPs
With low-code, you can test ideas in the market at lightning speed. Prototypes and MVPs are created in real time—user feedback flows directly into further development. This significantly reduces risk for new products.
Agile methods and iterative processes are optimally supported by low-code. Pilot projects in sales or customer service can be implemented without major investments. The statistics speak for themselves: 70% of companies see low-code as a driver of innovation.
You gain maximum flexibility to drive innovation in a targeted way—and stay one step ahead of competitors.
Use cases and practical examples for low-code in 2025
Low-code has long arrived in business reality. The range of use cases is growing rapidly—from automating everyday processes to modernizing complex IT landscapes. Especially in 2025, companies of all sizes and industries benefit from flexible, fast solutions that can be implemented without deep programming expertise.
Company-wide: From process automation to app development
With low-code, processes can be digitized and optimized across the company. Typical examples include automated vacation requests, digital invoice approvals, or custom business apps. Workflows are made more efficient, especially in HR, Finance, Sales, and Logistics.
- Automation of recurring tasks
- Rapid development of form flows
- Integration of different data sources
Both SMEs and large enterprises benefit. Studies show that 80% of companies already plan to deploy low-code projects by 2025 to act more flexibly and quickly.
Digital transformation and legacy modernization
Many companies face the challenge of modernizing old IT systems and manual processes. Low-code provides a bridge here: outdated Excel or Access solutions can be migrated to central platforms.
- Step-by-step integration of legacy IT
- Replacing manual processes with automated workflows
- Reduction of shadow IT
Gartner sees low-code as the key to successful digitization, as processes can be standardized while still being tailored to individual needs.
Customer and employee portals
Self-service portals are a prime example of low-code’s strengths. Companies use them to develop customer-friendly platforms and simplify internal processes for employees. Typical applications:
- Ticketing systems and service portals
- Knowledge bases for fast support
- Integration with CRM, ERP, or HR systems
Thanks to intuitive interface design, user satisfaction increases. Adjustments to new requirements are often completed in just a few minutes.
Automation and integration of third-party applications
Low-code enables seamless connection of SaaS solutions like Salesforce or Office 365. Data is automatically transferred between systems, reducing manual input.
- Automated data routing and synchronization
- Connecting external data sources via APIs
- Improved data quality and process reliability
iPaaS solutions are used, especially for complex integration scenarios. Companies save time and minimize sources of error.
Cross-industry use cases
The application possibilities of low-code are impressive across industries. In healthcare, it simplifies patient management; in the public sector, authorities are digitizing citizen services. In manufacturing, production processes are optimized; in retail, loyalty programs are implemented; and in the financial sector, compliance workflows are automated.
- Healthcare: Appointment booking, patient records
- Public sector: Digital forms
- Manufacturing: Maintenance management
According to Gartner, 65% of banks are already using low-code platforms. You can find more examples in the Anwendungsfällen für Low-Code-Plattformen.
filehub: Low-code automation for document workflows
A practical example of low-code is filehub. With this platform, you automate document workflows without having to program. You connect tools like Outlook, Docuware, or Teams and integrate them seamlessly into existing IT landscapes.
- GDPR-compliant and developed in Germany
- Rapid implementation thanks to templates and visual workflows
- Particularly suitable for teams with high compliance requirements
The result: no more manual file management, higher efficiency, and greater productivity in your company.
Step by step: Introducing low-code in your company
Getting started in the low-code world doesn’t begin with technology but with a clear strategy. The following six steps help you establish low-code systematically and successfully in your company.
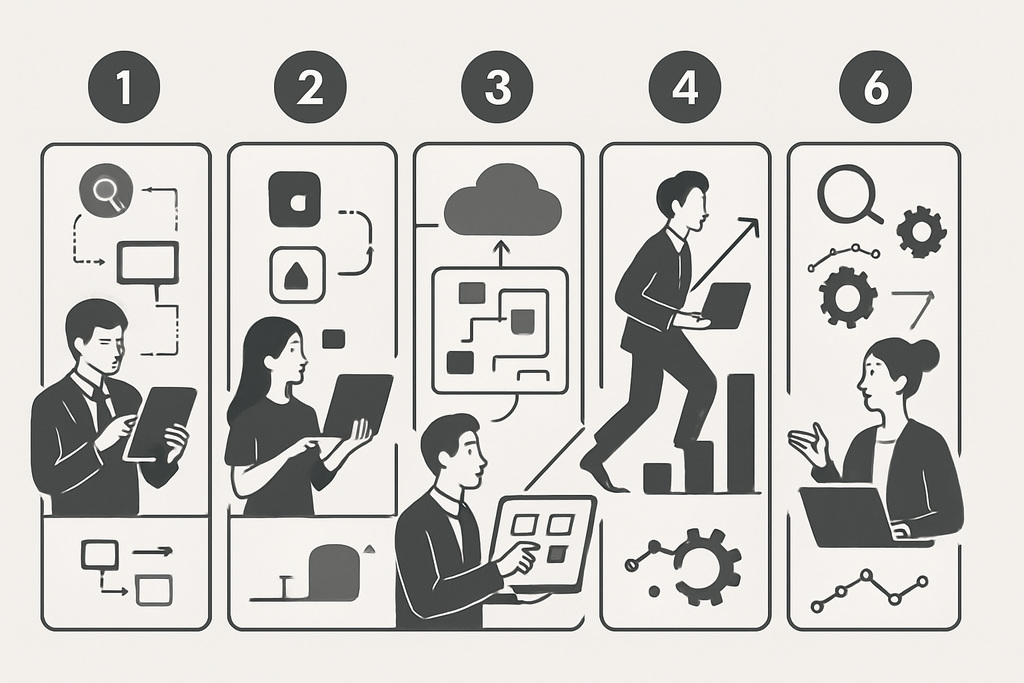
1. Needs analysis and goal definition
Every low-code initiative starts with a precise needs analysis. Identify processes that are time-consuming or prone to errors. Involve IT, business departments, and management early to get a comprehensive picture.
Set measurable goals, such as reduced processing time or lower error rates. Analyze the existing IT landscape and check interfaces relevant to automation. Prioritize use cases with the greatest leverage.
A requirements catalog helps define the project scope. Pilot projects, such as the automation of business processes, are ideal for getting started—you’ll quickly see the benefits of low-code.
2. Selecting the right low-code platform
Choosing the right low-code platform is crucial. Check which features you really need: Is simple app development enough, or do you need deep integration into existing systems? Pay attention to security features such as GDPR compliance and scalability.
Compare well-known providers like Mendix, OutSystems, Microsoft Power Apps, and filehub. Consider cost models, licensing, and support. The platform should offer intuitive operation and an active community.
Reference projects and customer reviews provide guidance. Industry-specific solutions can help you become productive faster. A careful comparison protects against limitations later on.
3. Pilot project and prototyping
Start with a manageable pilot project to test the low-code platform in practice. Choose a frequently used process that can be clearly delineated. Develop a first prototype or a minimum viable product (MVP), ideally with direct feedback from end users.
Use this opportunity to gain experience and strengthen collaboration between IT and the business. Document what worked well and where challenges arose.
For further inspiration, check out solutions for different business areas that show how low-code is used across various industries.
4. Scaling and integration into the IT landscape
Once the pilot has proven successful, it’s time to scale. Transfer the solutions you’ve developed to additional processes and departments. Low-code applications are typically integrated into existing systems like ERP, CRM, or DMS via APIs and connectors.
Build an internal center of excellence to pool know-how. Implement governance and security policies so development proceeds in a controlled and secure manner.
Automated testing and monitoring help ensure quality and stability. This is how low-code becomes a fixed part of your IT landscape.
5. Training, change management, and fostering acceptance
Low-code thrives on active employee involvement. Invest in targeted training for citizen developers and business departments. Promote collaboration between IT and the business, for example through joint workshops.
Clearly communicate the benefits of low-code and share success stories. Build an internal community to share knowledge and foster innovation.
Hackathons or internal competitions create incentives for creative solutions. Change management measures help reduce reservations and increase adoption.
6. Continuous optimization and innovation
Introducing low-code is not a one-off project but an ongoing process. Regularly review existing applications and optimize them based on user feedback.
Leverage new features and platform updates. Extend automation to additional processes, for example with AI-assisted workflows or mobile apps.
Monitor current market trends and best practices to keep your solutions future-proof. In this way, low-code becomes a driver of continuous innovation in your company.
Selection criteria, risks, and best practices for 2025
Selecting the right low-code platform is a key factor in the success of your digitization strategy. In addition to the obvious advantages, companies must also be aware of challenges, risks, and current market trends. Here you’ll find practical tips for choosing a platform, as well as proven best practices to stay a decisive step ahead with low-code in 2025.
Selection criteria for the right low-code platform
A powerful low-code platform must meet numerous requirements. Watch for the following criteria:
- Feature set: Does the platform support all desired workflows and processes?
- Extensibility: Can you easily add your own modules or integrations?
- Integrability: Does it connect smoothly to existing systems?
- Security & compliance: Are data protection standards like GDPR or C5 ensured?
- User-friendliness: Is the platform intuitive, even for citizen developers?
- Scalability: Can the solution grow with your company?
- Templates & marketplace: Are there reusable templates and an ecosystem?
- Support & community: Do you benefit from active exchange and quick help?
Visual process design is particularly important. Platforms like filehub offer intuitive workflows and visual process design that significantly accelerate low-code projects.
Typical challenges and risks
Even though low-code removes many hurdles, there are pitfalls:
- Limited customization: Very complex requirements can hit limits.
- Shadow IT: Uncontrolled development by business units carries risks.
- Vendor lock-in: Dependence on the platform provider can become problematic long term.
- Integration effort: The effort of connecting to legacy systems is often underestimated.
- Security gaps: Misconfiguration can lead to data protection issues.
- Adoption: Without change management, the rollout remains ineffective.
A structured approach minimizes these risks and ensures sustainable low-code success.
Best practices for a successful low-code rollout
To make your low-code project a success, you should follow these best practices:
- Governance: Define clear guidelines for citizen development.
- Collaboration: IT and business departments must work closely together.
- Iterative approach: Start with prototypes and continuously optimize.
- Use templates: Leverage templates and reusable building blocks.
- Training: Encourage knowledge sharing and continuous learning.
- Monitoring: Centrally monitor quality and security.
Successful companies rely on visual process design, as integrated in the workflows and visual process design approach, to efficiently manage low-code projects.
Market trends and outlook for 2025
The low-code market is growing dynamically. The following trends are emerging for 2025:
- AI integration: Automation and intelligent workflows are gaining importance.
- Data protection: Platforms are focusing more strongly on compliance and security.
- Cross-platform development: Web, mobile, and IoT are seamlessly connected.
- Citizen development: More and more business units are developing their own applications.
- Growth: Analysts such as Gartner and Forrester expect a sustained boom.
Innovations such as AI-assisted processes and new areas of application are shaping the future of low-code.
Key vendors and platforms compared
The low-code market is diverse. Here’s an overview of leading providers:
| Vendor | Special features | Target groups | Integrations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mendix | Comprehensive tools | Enterprises, SMEs | ERP, CRM, DMS |
| OutSystems | Scalability, AI | Enterprise | SaaS, legacy IT |
| Microsoft Power Apps | MS integration | All company sizes | Office 365, Dynamics |
| Appian | Case management | Banks, insurers | BPM, compliance |
| filehub | Document workflows | Compliance-oriented | Outlook, Teams, DMS |
When comparing, pay attention to licensing models, community, security, and industry-specific references. The right low-code platform forms the foundation for sustainable digital innovation.
You’ve now seen how low-code can simplify your workday and create real competitive advantages—without any programming skills. With solutions like filehub, you automate document and file processes, connect different systems, and save yourself tedious routine tasks. Especially if you value data protection, efficiency, and fast results, it’s worth getting started. Try it for yourself: filehub.one jetzt kostenlos testen and experience how simple automation can be for you and your team.


